Weather Patterns in a Semi-Arid Border Region: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
A semi-arid region located along a national border experiences a unique climate that is both diverse and challenging. Local weather is a critical factor in daily life, influencing agriculture, transportation, and overall well-being. This article provides a comprehensive overview of weather patterns in the region, examining historical trends, current conditions, and future projections. Understanding these dynamics helps appreciate the resilience and adaptability of local inhabitants.
Historical Weather Trends in the Region
Temperature Variations
The region has a semi-arid climate with hot summers and mild winters. Average annual temperatures align with similar semi-arid areas. Summer months often see high temperatures exceeding 100°F (38°C), while winter months bring milder conditions with occasional cooler spells.
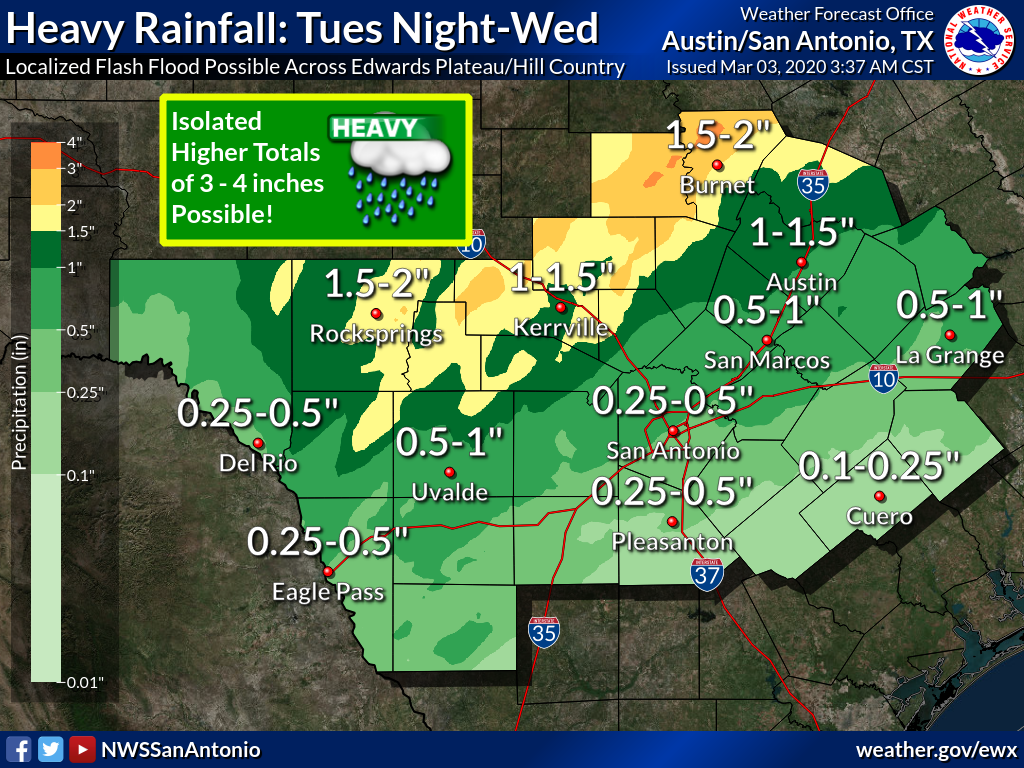
Precipitation Patterns
The region receives minimal annual precipitation, with most rainfall occurring during summer months. Dry conditions in winter contribute to its semi-arid climate.
Weather Events
The region is prone to various weather events, including thunderstorms, occasional tornadoes, and rare snowfall. Thunderstorms are most common in spring and summer, often accompanied by heavy rainfall and lightning. Tornadoes are rare but possible, while significant snowfall is extremely uncommon.
Current Weather Conditions
Climate Change Impacts
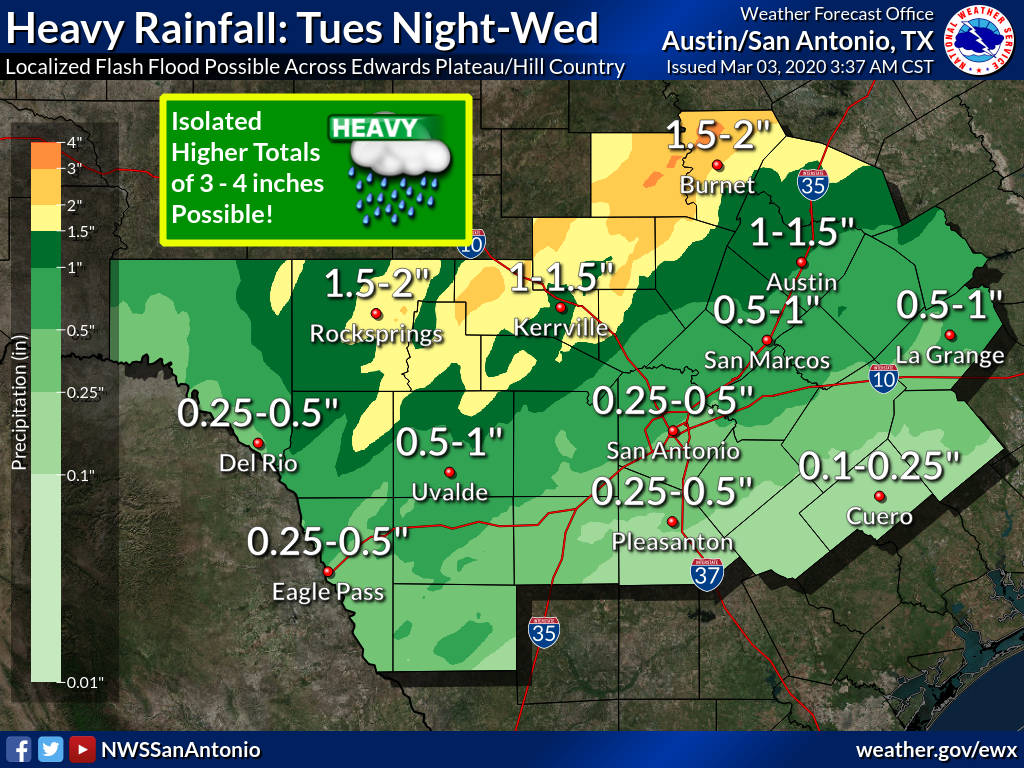
Recent studies indicate that climate change is affecting weather patterns globally, and this region is no exception. Official weather agencies report an increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. This has raised concerns about the future of local agriculture and overall resident well-being.
Current Trends
In recent years, the region has seen a slight rise in average temperatures and a decrease in precipitation. This trend aligns with global climate change patterns. Warmer temperatures have extended growing seasons for some crops but also increased drought and heat stress risks.
Future Projections
Climate Models
Climate models predict that future weather patterns in the region will continue to be shaped by climate change. International climate research bodies project warmer temperatures and potentially reduced precipitation in coming decades. These changes could have significant implications for the local economy and environment.

Adaptation Strategies
To mitigate potential climate change impacts, local authorities and residents are exploring various adaptation strategies. These include improving water conservation practices, developing drought-resistant crops, and updating building codes to withstand extreme weather events.
The Importance of Weather Monitoring
Public Safety
Accurate weather monitoring is crucial for public safety in the region. Timely warnings and forecasts from official agencies help residents prepare for and respond to severe weather events, such as tornadoes and flash floods.
Economic Impact

Local weather has a significant economic impact, especially on agriculture—a vital industry in the region. Weather conditions directly affect crop yields and market prices. Accurate forecasts help farmers make informed decisions about planting, irrigation, and harvesting.
Conclusion
The weather in this semi-arid border region is a complex, dynamic system influenced by local and global factors. Understanding historical trends, current conditions, and future projections is essential for regional well-being and economic stability. As climate change continues to affect weather patterns, it is critical for residents and policymakers to adapt and prepare for future challenges. This will help the region maintain its unique character and resilience.
Recommendations and Future Research
To enhance understanding of the region’s weather, the following recommendations are proposed:
1. Continue monitoring and analyzing weather patterns to identify trends and anomalies.

2. Invest in research to develop more accurate climate models for the region.
3. Educate the public about the importance of weather monitoring and preparedness.
4. Implement adaptation strategies to mitigate climate change impacts.
By following these recommendations, the region can remain a vibrant, resilient community capable of adapting to changing weather challenges.




